CAD(Carotid Artery Disease )Treatment in Dwarka, Delhi

Carotid Artery
The carotid arteries are the blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that carry blood to the head and brain.
Carotid artery disease
Carotid artery disease is a frequent source of the stroke. The lining of a normal carotid artery is smooth, but the inner walls of arteries narrowed by atherosclerosis can be very rough for irregular because fatty material called plaque collects inside the artery. Special components of the blood called platelets can dump on this irregular surfaces, small pieces if plaque or platelet clots can then travel to the brain, blocking blood flow to a portion of the blood flow to a portion of the brain and causing a stroke.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when a part of the brain is without blood for a prolonged period of time. That part of the brain becomes permanently injured. Causing difficulty with movement of the arms or legs, speech or vision. The specific disability that results is dependent upon which part of the brain and how large an area is affected. .
Transient ischemic attack
Sometimes called a mini- stroke, a translent ischemic attack (or TIA) is the temporary blockage of blood to a portion of the brain (or eye) that results in specific warning signs similar to stroke symptoms (see below) . The symptoms last less than a day, and generally this does not result in permanent injury to the brain. Although these symptoms resolve quickly, they are an important sign that someone is at high risk to develop a full- blown stroke if ignored. .
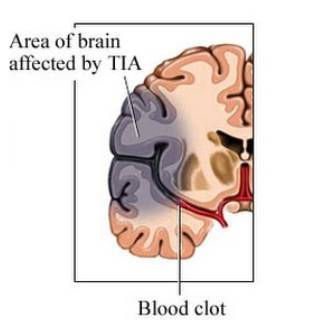
Symptoms of TIA or stroke
- Numbness, weakness,ad/or loss of coordination or paralayis of the arm or leg on one side of the body
- Drooping on one side of the mouth or face
- Blindness or loss of part of the vision in one eye (this may apper like a shade being drawn over the eye)
- Difficult speaking or inability to speak or understand written or spoken words

 High Cholesterol
High Cholesterol
 Diabetes
Diabetes
 High Blood Pressure
High Blood Pressure