INTRODUCTION
Diabetes and its challenges impact millions worldwide. One of the most dangerous complications is diabetic foot, which can lead to serious disability and, in extreme cases, require amputation. To manage diabetes, it’s crucial to understand its root causes, provide proper treatment, and take steps to prevent complications.
“Healthy feet are just a step away. In this blog, Dr. Tapish Sahu, a distinguished Peripheral Vascular Surgeon, sheds light on diabetic foot problems, covering causes, symptoms, and cutting-edge treatment options. Get expert insights to protect your foot health.”
DIABETIC FOOT WOUNDS: ARE YOU AT RISK?
A foot wound in a diabetic person refers to any injury or break in the skin on the foot. This can include cuts, blisters, or abrasions. Foot wounds can happen for many reasons, like poor blood flow and nerve damage (neuropathy).
Why do diabetics sustain foot wounds? A common question among people with diabetes is this one.
Diabetes can damage nerves and lower the blood supply to the feet, making them more vulnerable to injury and taking longer to heal. This implies that to prevent cuts and other issues, persons with diabetes need to take particular care when it comes to their feet. Without proper care, diabetic foot wounds can turn into foot ulcers also called diabetic foot sores. How can you spot a diabetic foot sore?
At first, it might look like a blister or burn. About 20-25% of people with diabetes will have a foot ulcer at some point in their lives.
OTHER CAUSES OF DIABETIC FOOT
Increase in blood sugar level – In individuals with diabetes, elevated blood sugar levels can lead to the deterioration of blood vessels and nerves located in the feet, resulting in diminished blood circulation and sensation. This raises the risk of foot problems. Untreated injuries and infections have the potential to deteriorate rapidly if not promptly addressed. Thus, diligent monitoring and timely treatment are essential.
- Infections – People with diabetes have a higher risk of infections. Even a minor foot injury like a cut or blister can become a serious infection if left untreated. Poor blood flow and nerve damage make these infections more likely. This increases the risk of tissue damage and other complications.
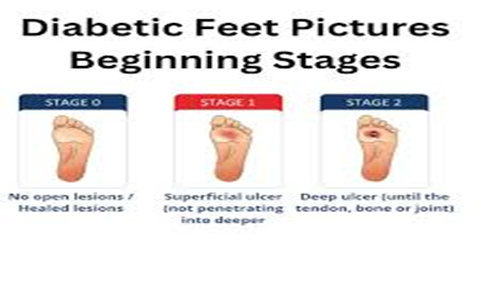
SIGN & SYMPTOMS OF DIABETIC FOOT
- Foot or ankle swelling
- Inflammation that takes much time to heal
- Leg pain
- Healing could take more time
- Ingrown toenails or fungal infections in toenails
- Presence of corns or calluses
- Dry cracks, especially around the heel
- Persistent or unusual foot odour
WOUND CARE FOR DIABETIC FOOT
Care for your feet, keep them clean, dry, and moisturized – Wash your feet daily without soaking them. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, and apply moisturizing cream.
Opt for closed-toe footwear with a spacious toe box- to avoid rubbing that can lead to sores or worsening wounds. Poorly fitting shoes often contribute to foot pain
Always keep your feet covered – and avoid going barefoot, even indoors. This provides a barrier against sharp objects, uneven surfaces, and other sources of injury. Even minor cuts can change into serious wounds due to compromised healing ability.
White socks made of cotton – Ensure they don’t have tight bands or thick seams that could irritate or rub against your skin.
Trim toenails – straight across and file down any sharp edges afterward.
LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS
For diabetic foot care, it is recommended that you consult a dietician who is trained to prepare healthy, tasty, and nutritious meals for people with diabetes. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains should make up the majority of your meals, and foods high in calories and saturated fat should be avoided. In addition to dietary changes, include exercise in your routine.
Exercise improves blood circulation, which can improve the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the wound. Weight loss can also help people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels.
CONCLUSION
“A proactive approach is necessary to prevent diabetic foot complications,” says Manipal Hospital Dwarka’s skilled peripheral vascular surgeon Dr. Tapish Sahu. “People with diabetes can take control of their foot health by being aware of the dangers related to nerve damage, poor blood flow, and foot problems. Regular visits to the doctor, appropriate footwear, and daily examinations of the feet are crucial. Furthermore, the risk of foot sores is considerably reduced by controlling blood sugar levels by good behaviors and medication adherence. People with diabetes can improve their health and reduce their risk of major complications by acting quickly and receiving professional assistance.”